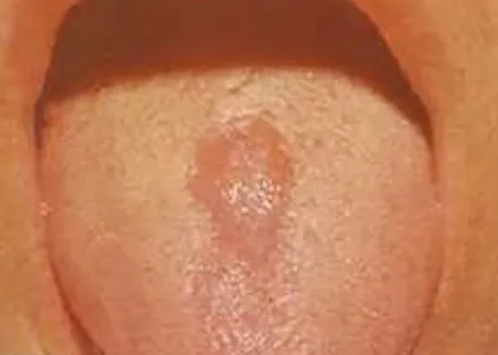
Glossitis, the inflammation of the tongue, can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, and vitamin deficiencies are among the common culprits. In this detailed health guide, we will explore glossitis associated with vitamin deficiencies, focusing on causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatments to restore oral health.
1. Understanding Glossitis: The Basics
Definition: Glossitis refers to the inflammation of the tongue, which can lead to changes in its color, texture, and overall appearance. It can be acute or chronic, and its causes are diverse, including infections, irritants, and nutritional deficiencies.
2. Vitamin Deficiencies Linked to Glossitis:
a. Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
- Symptoms: Glossitis related to vitamin B12 deficiency often presents with a sore, red, and swollen tongue. Other symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and tingling sensations in the extremities.
- Causes: Inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption issues, and certain medical conditions, such as pernicious anemia, can contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency.
b. Folate Deficiency:
- Symptoms: Folate deficiency may cause glossitis characterized by a smooth, red tongue. Additional symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Causes: Inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption, and certain medications, such as methotrexate, can lead to folate deficiency.
3. Symptoms of Glossitis:
a. Changes in Tongue Appearance:
- Color Changes: The tongue may appear red, smooth, or swollen.
- Surface Changes: Changes in the texture of the tongue, including a loss of papillae (tiny bumps on the tongue’s surface).
b. Discomfort and Pain:
- Soreness: Glossitis is often accompanied by soreness and discomfort.
- Burning Sensation: Some individuals may experience a burning sensation on the tongue.
c. Altered Taste:
- Metallic or Bitter Taste: Changes in taste perception may occur, leading to a metallic or bitter taste in the mouth.
4. Diagnosing Vitamin Deficiency Glossitis:
Medical History:
- Dietary Habits: A detailed inquiry into dietary habits helps identify potential vitamin deficiencies.
- Medical Conditions: Existing medical conditions or medications that may contribute to malabsorption are considered.
Physical Examination:
- Tongue Examination: A thorough examination of the tongue’s color, texture, and overall appearance.
- Oral Health Assessment: Checking for signs of infection or other oral health issues.
Laboratory Tests:
- Blood Tests: Assessing vitamin B12 and folate levels to identify deficiencies.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checking for anemia, which may indicate underlying nutritional deficiencies.
5. Treating Vitamin Deficiency Glossitis:
Supplementation:
- Vitamin B12 Supplements: For glossitis related to vitamin B12 deficiency, oral or injectable supplements are prescribed.
- Folate Supplements: Folate deficiency may be addressed with oral supplements.
Dietary Changes:
- Balanced Diet: Ensuring a diet rich in vitamin B12 and folate sources, including lean meats, fish, dairy, leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
- Nutrition Counseling: Consulting with a nutritionist to optimize dietary choices.
Addressing Underlying Causes:
- Treating Underlying Conditions: If glossitis is a symptom of an underlying condition, such as pernicious anemia, addressing the root cause is crucial for effective management.
- Medication Adjustments: In cases where medications contribute to nutritional deficiencies, adjustments may be made under medical supervision.
6. Managing Symptoms at Home:
Oral Hygiene:
- Gentle Brushing: Use a soft toothbrush to clean the tongue gently, avoiding harsh scrubbing.
- Mouthwash: Rinsing with a mild, alcohol-free mouthwash to maintain oral hygiene.
Hydration:
- Adequate Water Intake: Staying well-hydrated helps prevent dryness and discomfort.
Dietary Considerations:
- Avoiding Irritants: Limiting the intake of spicy or acidic foods that may exacerbate discomfort.
- Cooling Foods: Consuming cool or soothing foods, such as yogurt or ice cream, can provide relief.
7. Prevention of Vitamin Deficiency Glossitis:
Balanced Diet:
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Including a variety of nutrient-rich foods in the diet, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Supplementation as Needed: In consultation with healthcare providers, consider vitamin supplements if dietary intake is insufficient.
Regular Check-ups:
- Oral Health Check-ups: Regular dental check-ups help identify and address oral health issues promptly.
- Blood Tests: Periodic blood tests to monitor vitamin levels, especially for individuals at risk of deficiencies.
8. When to Seek Medical Attention:
Persistent Symptoms:
- If glossitis symptoms persist despite home care measures.
Signs of Complications:
- If additional symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath, develop.
Underlying Conditions:
- If glossitis is suspected to be a symptom of an underlying medical condition.
9. Conclusion: Nourishing Oral Health
Vitamin deficiency glossitis serves as a reminder of the intricate relationship between nutrition and oral health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments associated with this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to nourish their bodies and maintain vibrant oral well-being.
Regular dental check-ups, a balanced diet, and awareness of potential risk factors contribute to the prevention and management of vitamin deficiency glossitis. As we unlock the secrets of oral health, the journey towards a nourished and healthy tongue becomes an achievable goal for individuals seeking overall well-being.